The field of 3D printing has been rapidly evolving in recent years, with new technologies and systems emerging that offer greater precision, speed, and versatility. In this article, we will explore some of the latest and greatest 3D printing technologies and systems of 2023, including their features, advantages, and potential applications.
3D Printing Technologies and Systems
Continuous Liquid Interface Production (CLIP)
Continuous Liquid Interface Production (CLIP) is an innovative 3D printing technology that uses a combination of light and oxygen to create objects from a pool of liquid resin. By using a continuous flow of light and oxygen, CLIP can create objects at a much faster rate than traditional 3D printing methods, with greater precision and accuracy. CLIP is also capable of producing objects with a wider range of materials, including elastomers and ceramics.
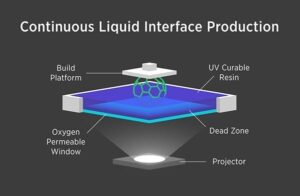
Potential applications of CLIP include the creation of medical devices and implants, where precision and accuracy are critical, as well as the production of complex mechanical parts and components.
Multi Jet Fusion (MJF)
Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) is a 3D printing technology developed by HP that uses a combination of thermal energy and binding agents to create objects from powdered materials. MJF is capable of producing objects at a much faster rate than traditional 3D printing methods, with greater precision and accuracy. It is also capable of producing objects with a wider range of materials, including nylon, polypropylene, and elastomers.
Potential applications of MJF include the production of automotive parts and components, where strength and durability are critical, as well as the creation of prosthetics and orthotics for medical applications.
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
Digital Light Processing (DLP) is a 3D printing technology that uses a projector to cure a liquid resin into solid objects. DLP is capable of producing objects at a much faster rate than traditional 3D printing methods, with greater precision and accuracy. It is also capable of producing objects with a wider range of materials, including dental resins and biocompatible materials.
Potential applications of DLP include the creation of dental molds and aligners, where precision and accuracy are critical, as well as the production of custom medical devices and implants.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is a 3D printing technology that uses a high-powered laser to fuse powdered materials into solid objects. SLS is capable of producing objects at a much faster rate than traditional 3D printing methods, with greater precision and accuracy. It is also capable of producing objects with a wider range of materials, including metals and ceramics.
Potential applications of SLS include the production of aerospace components and parts, where strength and durability are critical, as well as the creation of customized medical implants and devices.
Binder Jetting (BJ)
Binder Jetting (BJ) is a 3D printing technology that uses a binder to fuse powdered materials into solid objects. BJ is capable of producing objects at a much faster rate than traditional 3D printing methods, with greater precision and accuracy. It is also capable of producing objects with a wider range of materials, including metals and ceramics.
Potential applications of BJ include the production of jewelry and decorative objects, where intricate and complex designs are required, as well as the creation of customized medical implants and devices.
Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF)
Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) is a 3D printing technology that uses a heated nozzle to extrude melted plastic filament into solid objects. FFF is capable of producing objects at a much faster rate than traditional 3D printing methods, with greater precision and accuracy. It is also capable of producing objects with a wider range of materials, including flexible and biodegradable materials.
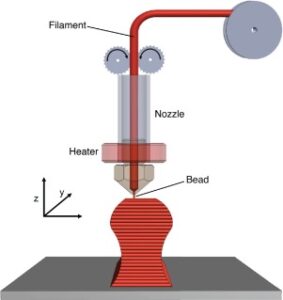
Potential applications of FFF include the production of consumer products and gadgets, where customization and personalization are important, as well as the creation of prototypes and models for industrial and mechanical applications.
Another trend in 3D printing is the development of hybrid systems that combine different technologies and processes to create even more advanced and versatile systems. For example, some systems combine traditional 3D printing with CNC machining or injection moulding to create objects with even greater precision and complexity.
As the field of 3D printing continues to evolve, there are also challenges and considerations to keep in mind. For example, there are still limitations in terms of the materials that can be used in 3D printing, as well as challenges around intellectual property and quality control.
However, with careful planning and consideration, 3D printing technologies have the potential to transform the way we approach product design and manufacturing, offering greater flexibility, speed, and customization. As we move forward into the future, it will be exciting to see how 3D printing technologies continue to evolve and transform the world around us.
There are also exciting developments in the field of bioprinting, which is the use of 3D printing technology to create human tissue and organs. While this technology is still in its early stages, it has the potential to revolutionize the field of medicine, offering new possibilities for organ transplant and regeneration.
Another important trend in 3D printing is sustainability, with a growing focus on using eco-friendly materials and processes. This includes the use of recycled materials, biodegradable materials, and renewable energy sources. As the world becomes more environmentally conscious, 3D printing technologies will play an important role in creating a more sustainable future.
In terms of applications, 3D printing is being used in a wide range of industries, from aerospace and automotive to healthcare and fashion. For example, in the aerospace industry, 3D printing is being used to create lightweight and complex components that are difficult to produce using traditional methods. In the healthcare industry, 3D printing is being used to create customized prosthetics, implants, and surgical tools.
In the fashion industry, 3D printing is being used to create unique and intricate designs, as well as to produce sustainable and eco-friendly clothing. Some designers are even using 3D printing to create entire garments, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in terms of design and production.
Conclusion
The latest and greatest 3D printing technologies and systems of 2023 offer a range of advantages in terms of speed, precision, and versatility. From CLIP and MJF to DLP and SLS, these technologies offer a wide range of potential applications in fields such as aerospace, medicine, and consumer products. As 3D printing continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovation and growth in the field, with new materials, processes, and systems emerging that push the boundaries of what is possible.





